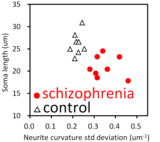
 Volumetric changes in the superior temporal gyrus and anterior cingulate cortex have been repeatedly reported in studies on schizophrenia. We analyzed nanometer-scale 3D structures of brain tissues of these areas by using synchrotron radiation nano-CT. The obtained results indicated that 1) neurites in both areas become thin and tortuous in schizophrenia and that 2) somata become small in schizophrenia. The frequency distribution of neurite curvatures had a broad profile in the schizophrenia cases, whereas the control cases showed sharp peaks. In the scatter diagram of the cell body length and the standard deviation of neurite curvatures of the anterior cingulate coretx (figure left), the schizophrenia and control cases form separate clusters, indicating that all 16 cases analyzed in this study can be assigned to either the schizophrenia or control group simply by using this diagram. The cingulate / temporal ratio of the standard deviation of neurite curvatures showed a strong positive correlation with the auditory hallucination score. Hence, the neuronal alterations observed in the schizophrenia cases should be a target for novel treatments of schizophrenia.
Original paper 1,
paper 2.
This study was appeared in PsyPost.
Our related study (
Transl.Psychiatry 2019
2021
) was news released from
Argonne National Lab and widely mentioned in the
news media.
It's featured in the
APS highlights
and ranked top 5 percentile with Altmetrics.
YouTube: 3D image - Network.
We also found that brain capillary structures correlate with neuron structures: DOI YouTube.
Volumetric changes in the superior temporal gyrus and anterior cingulate cortex have been repeatedly reported in studies on schizophrenia. We analyzed nanometer-scale 3D structures of brain tissues of these areas by using synchrotron radiation nano-CT. The obtained results indicated that 1) neurites in both areas become thin and tortuous in schizophrenia and that 2) somata become small in schizophrenia. The frequency distribution of neurite curvatures had a broad profile in the schizophrenia cases, whereas the control cases showed sharp peaks. In the scatter diagram of the cell body length and the standard deviation of neurite curvatures of the anterior cingulate coretx (figure left), the schizophrenia and control cases form separate clusters, indicating that all 16 cases analyzed in this study can be assigned to either the schizophrenia or control group simply by using this diagram. The cingulate / temporal ratio of the standard deviation of neurite curvatures showed a strong positive correlation with the auditory hallucination score. Hence, the neuronal alterations observed in the schizophrenia cases should be a target for novel treatments of schizophrenia.
Original paper 1,
paper 2.
This study was appeared in PsyPost.
Our related study (
Transl.Psychiatry 2019
2021
) was news released from
Argonne National Lab and widely mentioned in the
news media.
It's featured in the
APS highlights
and ranked top 5 percentile with Altmetrics.
YouTube: 3D image - Network.
We also found that brain capillary structures correlate with neuron structures: DOI YouTube.
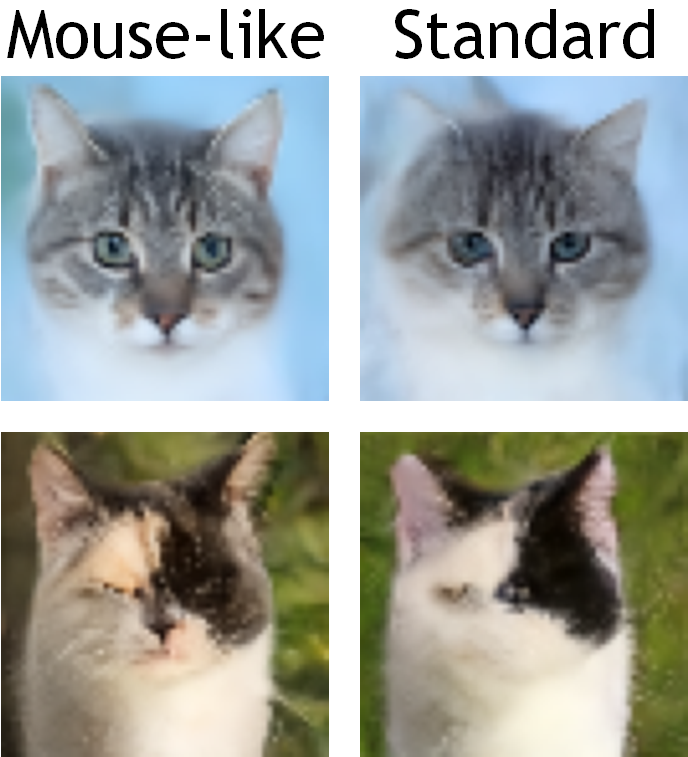 Then we implemented the findings from the synchrotron radiation study on brain tissues into the artificial neural network including generative AIs. The analysis of brain tissues of human and mouse indicated that mouse neuronal somata are smaller and neurites are thinner than those of human neurons. We incorporated those characteristics of mouse neurons in convolutional layers of a generative adversarial network (GAN) and a denoising diffusion implicit model (DDIM), which were then subjected to image generation tasks using photo datasets of cat faces, cheese, human faces, and birds. The mouse-mimetic GAN outperformed a standard GAN in the image generation task using the cat faces and cheese photo datasets, but underperformed for human faces and birds. The mouse-mimetic DDIM gave similar results, suggesting that the nature of the datasets affected the results. Analyses of the used datasets indicated differences in their image entropy, which should influence the number of parameters required for image generation. The preferences of the mouse-mimetic AIs coincided with the impressions commonly associated with mice. The relationship between the neuronal network and brain function should be investigated by implementing other biological findings in artificial neural networks.
DOI
arXiv
github repo
Then we implemented the findings from the synchrotron radiation study on brain tissues into the artificial neural network including generative AIs. The analysis of brain tissues of human and mouse indicated that mouse neuronal somata are smaller and neurites are thinner than those of human neurons. We incorporated those characteristics of mouse neurons in convolutional layers of a generative adversarial network (GAN) and a denoising diffusion implicit model (DDIM), which were then subjected to image generation tasks using photo datasets of cat faces, cheese, human faces, and birds. The mouse-mimetic GAN outperformed a standard GAN in the image generation task using the cat faces and cheese photo datasets, but underperformed for human faces and birds. The mouse-mimetic DDIM gave similar results, suggesting that the nature of the datasets affected the results. Analyses of the used datasets indicated differences in their image entropy, which should influence the number of parameters required for image generation. The preferences of the mouse-mimetic AIs coincided with the impressions commonly associated with mice. The relationship between the neuronal network and brain function should be investigated by implementing other biological findings in artificial neural networks.
DOI
arXiv
github repo
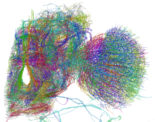 We have also reported a three-dimensional analysis of the brain network of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster by synchrotron-radiation nanotomography. A skeletonized wire model of the left half of the brain network was built by tracing the 3D image of the brain network. The obtained models of neuronal processes were classified into groups on the basis of their structures. The model structure indicated that the Drosophila brain is composed of networks with different complexity and extensity depending on the brain regions. Simple networks in the optic lobe should be appropriate for relaying information straightforwardly while intricate and widespread networks mainly in the central brain can integrate information from a number of brain regions. These structures of the reconstructed networks provide a basis for understanding how the Drosophila brain works. An article reviewing this study appeared in MIT Technology Review.
DOI
PubMed
arXiv
YouTube
We have also reported a three-dimensional analysis of the brain network of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster by synchrotron-radiation nanotomography. A skeletonized wire model of the left half of the brain network was built by tracing the 3D image of the brain network. The obtained models of neuronal processes were classified into groups on the basis of their structures. The model structure indicated that the Drosophila brain is composed of networks with different complexity and extensity depending on the brain regions. Simple networks in the optic lobe should be appropriate for relaying information straightforwardly while intricate and widespread networks mainly in the central brain can integrate information from a number of brain regions. These structures of the reconstructed networks provide a basis for understanding how the Drosophila brain works. An article reviewing this study appeared in MIT Technology Review.
DOI
PubMed
arXiv
YouTube
 Spatial resolution is the fundamental parameter in structural sciences. We developed a method for estimating the spatial resolution of real images from a logarithmic intensity plot in the Fourier domain. The logarithmic intensity plots of test images indicated that the full width at half maximum of a Gaussian point spread function can be estimated from the images themselves. The spatial resolution of imaging X-ray nanotomography using Fresnel zone-plate optics was estimated with this method. A cross section of a test object visualized with the nano-CT indicated that square-wave patterns up to 120-nm pitch were resolved. The logarithmic intensity plot was calculated from a nano-CT cross section of brain tissue. The full width at half maximum of the point spread function estimated from the plot coincided with the resolution determined from the test object. These results indicated that the logarithmic intensity plot in the Fourier domain provides an alternative measure of the spatial resolution without explicitly defining a noise criterion.
DOI
PubMed
arXiv
Spatial resolution is the fundamental parameter in structural sciences. We developed a method for estimating the spatial resolution of real images from a logarithmic intensity plot in the Fourier domain. The logarithmic intensity plots of test images indicated that the full width at half maximum of a Gaussian point spread function can be estimated from the images themselves. The spatial resolution of imaging X-ray nanotomography using Fresnel zone-plate optics was estimated with this method. A cross section of a test object visualized with the nano-CT indicated that square-wave patterns up to 120-nm pitch were resolved. The logarithmic intensity plot was calculated from a nano-CT cross section of brain tissue. The full width at half maximum of the point spread function estimated from the plot coincided with the resolution determined from the test object. These results indicated that the logarithmic intensity plot in the Fourier domain provides an alternative measure of the spatial resolution without explicitly defining a noise criterion.
DOI
PubMed
arXiv
 Mizutani attaching a sample on the rotation stage of the 32-ID beamline of APS, Argonne National Lab. If you use human tissue samples, your operating procedure must be approved by the institutional committee beforehand. The procedure may ask you to wear personal protective equipments.
Mizutani attaching a sample on the rotation stage of the 32-ID beamline of APS, Argonne National Lab. If you use human tissue samples, your operating procedure must be approved by the institutional committee beforehand. The procedure may ask you to wear personal protective equipments.